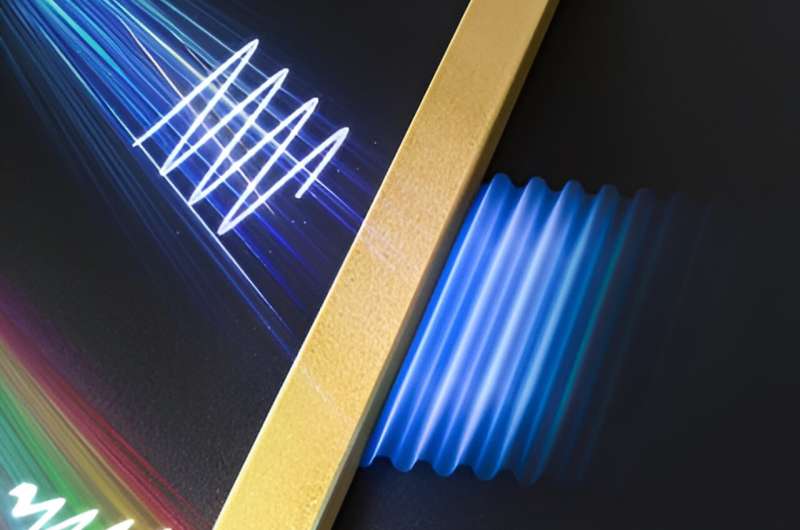
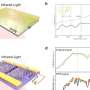
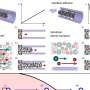
Figure 1. Schematic of polariton propagations under real frequency and synthesized complex frequency excitation. While polariton waves at real frequencies have limited propagation distance, combining propagation waves from different real frequencies based on complex frequencies of incidence can achieve nearly lossless propagation. Credit: Nature Materials (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41563-023-01787-8
A collaborative research team co-led by Professor Shuang Zhang, the Interim Head of the Department of Physics, The University of Hong Kong (HKU), along with Professor Qing DAI from National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, China, has introduced a solution to a prevalent issue in the realm of nanophotonics, which is the study of light at an extremely small scale.
Their findings, recently published in Nature Materials, propose a synthetic complex frequency wave (CFW) approach to address optical loss in polariton propagation.
These findings offer practical solutions, such as more efficient light-based devices for faster and more compact data storage and processing in devices such as computer chips and data storage devices, and improved accuracy in sensors, imaging techniques, and security systems.
Surface plasmon polaritons and phonon polaritons offer advantages such as efficient energy storage, local field enhancement, and high sensitivities, benefitting from their ability to confine light at small scales. However, their practical applications are hindered by the issue of ohmic loss, which causes energy dissipation when interacting with natural materials.
Over the past three decades, this limitation has impeded progress in nanophotonics for sensing, superimaging, and nanophotonic circuits. Overcoming ohmic loss would significantly enhance device performance, enabling advancement in sensing technology, high-resolution imaging, and advanced nanophotonic circuits.
Professor Shuang Zhang, corresponding author of the paper, explained the research focus, "To address the optical loss challenge in key applications, we have put forward a practical solution. By employing a novel synthetic complex wave excitation, we can achieve virtual gain and counteract the intrinsic loss of the polariton system. To validate this approach, we applied it to the phonon polariton propagation system and observed a significant improvement in polariton propagation."
"We demonstrated our approach by conducting experiments using phonon polariton material, such as hBN and MoO3, in the optical frequency range. As expected, we obtained nearly lossless propagation distance consistent with our theoretical predictions," added Dr. Fuxin Guan, the paper's first author and a Postdoctoral Fellow at the Department of Physics at HKU.
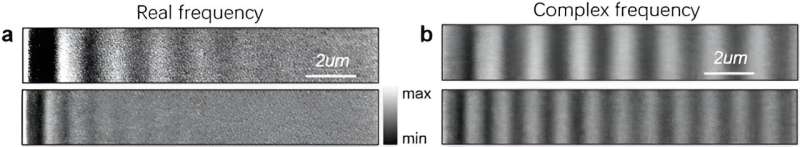
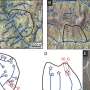
Figure 2. 1D Polariton propagation (from left to right) using hBN film operating at optical frequency. (a) Real frequency images show obvious decay field profile at propagation direction. (b) Complex frequency measurements provide almost non-dissipative propagation behavior. Credit: Nature Materials (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41563-023-01787-8
Multi-frequency approach to overcome optical loss
In this research, the team developed a novel multiple-frequency approach to address energy loss in polariton propagation. They used a special type of wave called "complex frequency waves" to achieve virtual gain and compensate for the loss in an optical system. While a regular wave maintains a constant amplitude or intensity over time, a complex frequency wave exhibits both oscillation and amplification simultaneously. This characteristic allows for a more comprehensive representation of wave behavior and enables compensation for energy loss.
While frequency is commonly perceived as a real number, it can also have an imaginary part. This imaginary part tells us how the wave either gets stronger or weaker over time. Waves with a complex frequency featuring a negative (positive) imaginary part decay (amplify) over time. However, directly carrying our measurement under the excitation of complex frequency waves in optics is challenging because it requires complex time-gated measurements.
To overcome this, the researchers employed the Fourier Transformation mathematical tool to break down a truncated complex frequency wave (CFW) into multiple components with individual frequencies.
More information: Fuxin Guan et al, Compensating losses in polariton propagation with synthesized complex frequency excitation, Nature Materials (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41563-023-01787-8
Journal information: Nature Materials
Provided by The University of Hong Kong