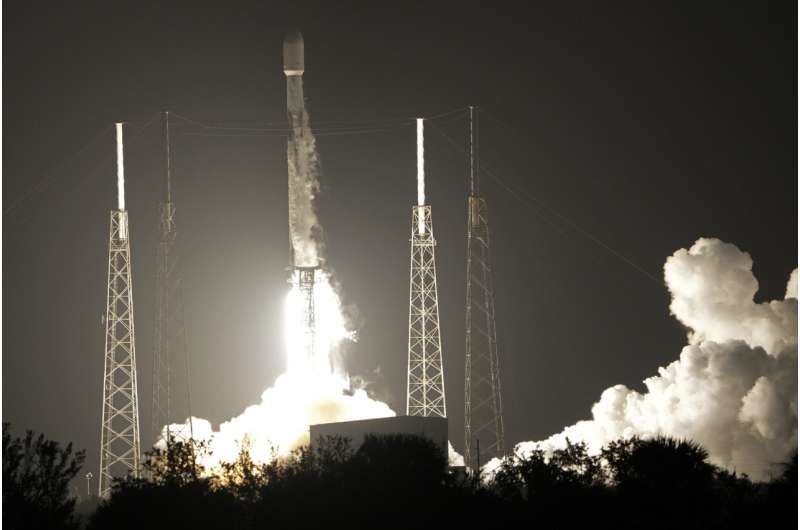
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, with a payload including two lunar rovers from Japan and the United Arab Emirates, lifts off from Launch Complex 40 at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Dec. 11, 2022. But later in April 2023, the spacecraft from a Japanese company apparently crashed while attempting to land on the moon. Japan now hopes to make the world's first "pinpoint landing" on the moon early Saturday, Jan. 20, 2024, joining a modern push for lunar contact with roots in the Cold War-era space race between the United States and the Soviet Union. Credit: AP Photo/John Raoux, File
As Japan's space agency prepares for its first moon landing early Saturday, it's aiming to hit a very small target.
The Smart Lander for Investigating Moon, or SLIM, is a lightweight spacecraft about the size of a passenger vehicle. It's using "pinpoint landing" technology that promises far greater control than any previous moon landing.
While most previous probes have used landing zones about 10 kilometers (six miles) wide, SLIM is aiming at a target of just 100 meters (330 feet).
It's the fruit of two decades of work on precision technology by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, or JAXA. If successful, it would make Japan the fifth country to land on the moon, after the United States, Russia, China and India.
The mission's main goal is to test new landing technology that would allow moon missions to land "where we want to, rather than where it is easy to land," JAXA has said. After landing, the spacecraft will seek clues about the origin of the moon, including analyzing minerals with a special camera.
The SLIM, equipped with a pad to cushion impact, aims to land near the Shioli crater, near a region covered in volcanic rock.
The closely watched mission comes only 10 days after a moon mission by a U.S. private company failed when the spacecraft developed a fuel leak hours after the launch.
SLIM lowered its orbit to 15 kilometers (more than nine miles) above the lunar surface on Friday, from which it will make a final approach to a touchdown, JAXA said. The attempt is scheduled 20 minutes after midnight Tokyo time on Saturday.
JAXA said everything was going well, and it issued a final go late Friday for a planned touchdown.
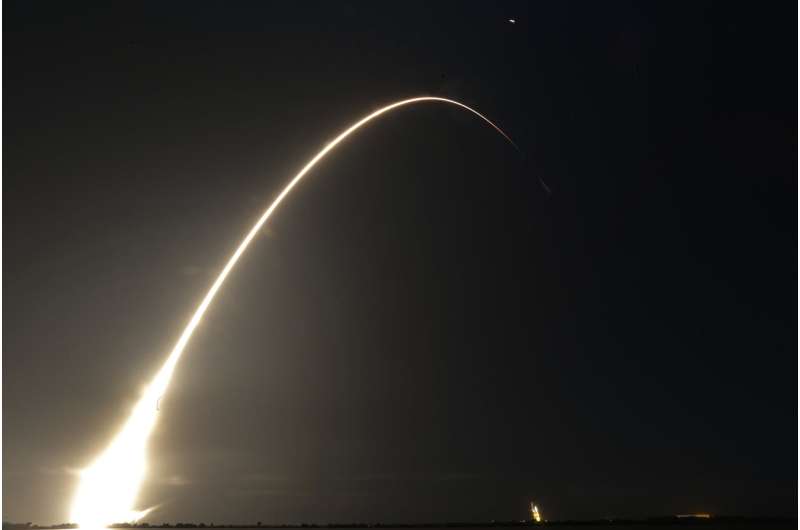
This time exposure photo shows a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, with a payload including two lunar rovers from Japan and the United Arab Emirates, launching from Launch Complex 40 at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Dec. 11, 2022. But later in April 2023, the spacecraft from a Japanese company apparently crashed while attempting to land on the moon. Japan now hopes to make the world's first "pinpoint landing" on the moon early Saturday, Jan. 20, 2024, joining a modern push for lunar contact with roots in the Cold War-era space race between the United States and the Soviet Union. Credit: AP Photo/John Raoux, File
Nicknamed the Moon Sniper, it was launched on a Mitsubishi Heavy H2A rocket in September. It initially orbited Earth and entered lunar orbit on Dec. 25.
Japan also hopes a success will help regain confidence for its space technology after a number of failures. A spacecraft designed by a Japanese company crashed during a lunar landing attempt in April, and a new flagship rocket failed its debut launch in March.
JAXA has a track record with difficult landings. Its unmanned Hayabusa2 spacecraft, launched in 2014, touched down twice on the 900-meter-long (3,000-foot-long) asteroid Ryugu, collecting samples that were returned to Earth.
Experts say a success of SLIM's pinpoint landing, especially on the moon, would raise Japan's profile in the global space technology race.
Takeshi Tsuchiya, aeronautics professor at the Graduate School of Engineering at the University of Tokyo, said it was important to confirm the accuracy of landing on a targeted area for the future of moon explorations.
"It is necessary to show the world that Japan has the appropriate technology in order to be able to properly assert Japan's position in lunar development," he said. The moon is important from the perspective of explorations of resources, and it can also be used as a base to go to other planets, like Mars, he said.
SLIM is carrying two small autonomous probes—lunar excursion vehicles LEV-1 and LEV-2, which will be released just before landing.
LEV-1, equipped with an antenna and a camera, is tasked with recording SLIM's landing. LEV-2, is a ball-shaped rover equipped with two cameras, developed by JAXA together with Sony, toymaker Tomy and Doshisha University.
JAXA will broadcast a livestream of the landing, while space fans will gather to watch the historic moment on a big screen at the agency's Sagamihara campus southwest of Tokyo.
© 2024 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.