This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Eliminating hidden hunger: How biofortification can improve nutrition at home and abroad
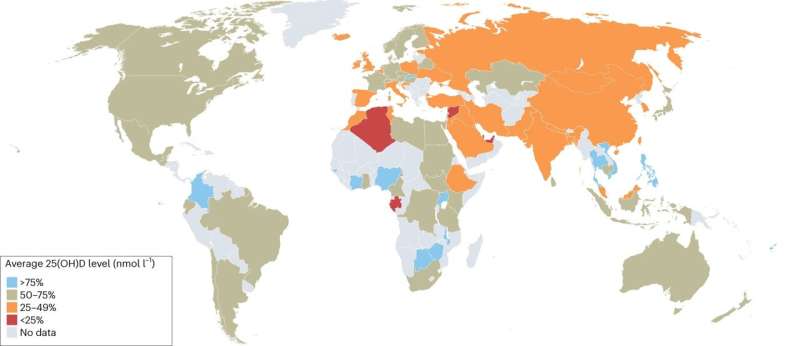
Researchers from the John Innes Centre and the Max-Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology are calling for biofortification to play an integrated role in national and international food strategies to relieve the global problem of hidden hunger.
This recommendation is made in a perspective article published in Nature Food, which examines the issue of malnutrition caused by micronutrient deficiencies and makes a case for continued efforts to biofortify crops with key micronutrients such as provitamin D/vitamin D, vitamin B12, and iron to improve nutrition.
Globally, the number of people who are undernourished in terms of calories has reduced by almost 50 percent in recent decades. Staple crops address this hunger for many; however, they do not provide the micronutrients required for adequate nutrition, especially after processing.
It is estimated that 2 billion people are affected by micronutrient deficiency, or "hidden hunger," and the real total could be even greater. Iron deficiency alone is estimated to occur in more than 50 percent of the global population.
Recent media reports have suggested that this is not just a problem in less well-off nations—with a reported rise in UK hospital admissions related to nutrient deficiencies and a headteacher in an East of England school revealing the plight of malnourished children in their classrooms.
This builds on evidence that consumers are receptive to higher-quality, natural, more nutritious food products, so long as taste and price are not compromised.
The first author of the article, Dr. Jie Li from the John Innes Centre, said, "We want to highlight that biofortification strategies present an opportunity to reduce hidden hunger around the world. Consumer traits like nutritional value must be combined with traits which benefit farmers and food producers to ensure nutritional improvements are integrated into the global food system."
A key strategy they put forward promotes the inclusion of biofortified plants in foods that feature prominently in daily diets. The proposed "food as medicine" approach would reduce the vast sums spent by national health services to treat conditions and diseases that occur because of micronutrient deficiency.
Professor Cathie Martin, FRS, co-author of the article, says, "Promoting the inclusion of sustainably produced, biofortified foods in commonplace diets would represent a key step towards reducing the economic and societal burdens emerging from health care costs associated with micronutrient malnutrition."
Biofortification, the process of increasing the micronutrient content of a food crop through selective breeding, genetic modification, or enriched fertilizers, was first proposed in the 1990s as a low-cost, sustainable way of enhancing the mineral and vitamin contents of staple food crops to address micronutrient malnutrition.
New genetic technologies such as gene editing have emerged as promising alternatives for biofortifying staple foods.
The significant role that biofortification might play in improving national and international health has been recognized by UKRI/BBSRC with investment in a 1.9m Biofortification Hub led by the John Innes Centre and the Quadram Institute on the Norwich Research Park. The Biofortification Hub offers seed funding for innovative projects that link academic research with industry in seeking to improve the nutritional density of food.
"Food production has been incentivized to focus on calorific content and yield at the expense of nutritional density with negative consequences for human health."
"Biofortification is one useful tool which we must use to redress this imbalance," says Dr. Jie Li.
More information: Jie Li et al, Biofortification's contribution to mitigating micronutrient deficiencies, Nature Food (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s43016-023-00905-8
Journal information: Nature Food
Provided by John Innes Centre