ATLAS reports first observation of WWW production

The ATLAS Collaboration at CERN announces the first observation of "WWW production": The simultaneous creation of three massive W bosons in high-energy Large Hadron Collider (LHC) collisions.
As a carrier particle of the electroweak force, the W boson plays a crucial role in the Standard Model of particle physics. Though discovered nearly four decades ago, the W boson continues to provide physicists with new avenues for exploration. In particular, its study has allowed scientists to test the Standard Model through precise measurements of rare processes.
Today, at the EPS-HEP Conference 2021, the ATLAS Collaboration announced the first observation of a rare process: The simultaneous production of three W bosons. ATLAS researchers analyzed the full LHC Run-2 dataset, recorded by the detector between 2015 and 2018, to observe the process with a statistical significance of 8.2 standard deviations—well above the 5 standard-deviation threshold needed to claim observation. This result follows an earlier observation by the CMS Collaboration of inclusive three weak boson production.
Achieving this level of precision was no mean feat. Physicists analyzed around 20 billion collision events recorded and pre-filtered by the ATLAS experiment, looking for just a few hundred events expected from the WWW process. These events were buried in almost five times more background events that mimic the signal signature.

As one of the heaviest known elementary particles, the W boson is able to decay in several different ways. ATLAS physicists focused their search on the four WWW decay modes with the best discovery potential, due to their reduced number of background events. In three of these modes, two W bosons decay into charged leptons (electrons or muons), carrying the same positive or negative charge, and neutrinos, while the third W boson decays into a pair of light quarks (called the "2l channels"). In the fourth decay mode, all the three W bosons decay into a charged lepton and neutrino (called the "3l channel").
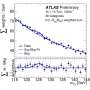
To pick out the WWW signal from the large number of background events, researchers utilized a machine learning technique called Boosted Decision Trees (BDTs). BDTs can be trained to identify specific signals in the ATLAS detector, spotting small—but key—differences between well-known variables. For this analysis, physicists trained two BDTs: One for the 2l channels using 12 well-modeled variables, and the other for the 3l channel with 11 variables.
The figure shows the BDT distribution for the 3l channel. The improved separation power between signal and background provided by the BDT—along with the massive dataset provided by Run 2 of the LHC—improved the precision of the overall measurement and enabled the first observation of http://www. The observed significance of the measurement is 8.2 standard deviations. The cross section was measured to be 850 ± 100 (statistical) ± 80 (systematic) fb, compared to the Standard Model predicted cross-section of 511 ± 42 fb.
This exciting measurement also allows physicists to look for hints of new interactions that might exist beyond the current energy reach of the LHC. In particular, physicists can use the WWW production process to study the quartic gauge boson coupling, a key parameter of the Standard Model. New particles could alter the quartic gauge boson coupling through quantum effects, modifying the WWW production cross section. The continued study of WWW and other electroweak processes provides an enticing road ahead.
More information: Observation of WWW production in proton–proton collisions at 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector (ATLAS-CONF-2021-039): atlas.web.cern.ch/Atlas/GROUPS … ATLAS-CONF-2021-039/
Provided by ATLAS Experiment