Hostile teachers can lose students 5 percent on test scores

Teachers who antagonize their students by belittling them, showing favoritism, or criticizing their contributions can damage their learning potential, a new study warns.
Investigating the influence of teacher 'misbehavior' on student learning, a team of communication experts set up a teaching experiment in which almost 500 undergraduate students watched a video of a lecture.
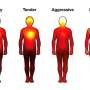
Randomly split into two groups, the participants watched either a lesson with teacher antagonism present, or a standard lesson, without antagonism. They then answered a series of questions about the content, before completing a multiple-choice test.
Comparing the test scores of the two groups, researchers found that the antagonism group performed worse than the standard group. Test scores were up to 5% lower for those who watched the lesson with antagonism because they disliked what they were learning.
What's more, students who faced teacher hostility were less likely to put as much effort into learning, and were unwilling to take part in future courses taught by that teacher.
Study leader Dr. Alan Goodboy stressed the negative longer-term consequences of this teacher misbehavior for student learning: "Even slight antagonism, coupled with otherwise effective teaching, can demotivate students from being engaged and hinder their learning opportunities. So even one bad day of teaching can ruin a student's perception of the teacher and create an unnecessary roadblock to learning for the rest of the term."
Teachers should therefore be especially careful to prevent negative behaviour seeping into the classroom.
"Antagonism can come into classrooms unexpectedly and suddenly, even without the knowledge of the teachers themselves," Goodboy added.
"We therefore need to ensure that future teachers are better equipped to recognize when antagonism may be creeping in, focusing on how antagonism manifests itself and working on developing more positive ways of interacting with students, even during times of disagreement."
More information: Communication Education, DOI: 10.1080/03634523.2018.1465192
Provided by Taylor & Francis