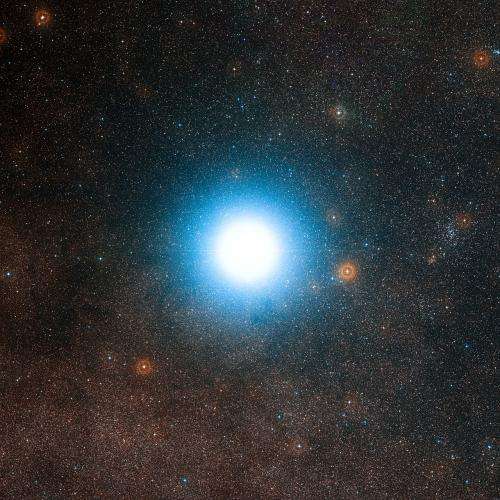
This artist’s impression shows the planet orbiting the star Alpha Centauri B, a member of the triple star system that is the closest to Earth. Alpha Centauri B is the most brilliant object in the sky and the other dazzling object is Alpha Centauri A. Our own Sun is visible to the upper right. The tiny signal of the planet was found with the HARPS spectrograph on the 3.6-metre telescope at ESO’s La Silla Observatory in Chile. Credit: ESO/L. Calçada
(Phys.org)—European astronomers have discovered a planet with about the mass of the Earth orbiting a star in the Alpha Centauri system—the nearest to Earth. It is also the lightest exoplanet ever discovered around a star like the Sun. The planet was detected using the HARPS instrument on the 3.6-metre telescope at ESO's La Silla Observatory in Chile. The results will appear online in the journal Nature on 17 October 2012.
Alpha Centauri is one of the brightest stars in the southern skies and is the nearest stellar system to our Solar System—only 4.3 light-years away. It is actually a triple star—a system consisting of two stars similar to the Sun orbiting close to each other, designated Alpha Centauri A and B, and a more distant and faint red component known as Proxima Centauri. Since the nineteenth century astronomers have speculated about planets orbiting these bodies, the closest possible abodes for life beyond the Solar System, but searches of increasing precision had revealed nothing. Until now.
"Our observations extended over more than four years using the HARPS instrument and have revealed a tiny, but real, signal from a planet orbiting Alpha Centauri B every 3.2 days," says Xavier Dumusque (Geneva Observatory, Switzerland and Centro de Astrofisica da Universidade do Porto, Portugal), lead author of the paper. "It's an extraordinary discovery and it has pushed our technique to the limit!"
This wide-field view of the sky around the bright star Alpha Centauri was created from photographic images forming part of the Digitized Sky Survey 2. The star appears so big just because of the scattering of light by the telescope's optics as well as in the photographic emulsion. Alpha Centauri is the closest star system to the Solar System. Credit: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2
The European team detected the planet by picking up the tiny wobbles in the motion of the star Alpha Centauri B created by the gravitational pull of the orbiting planet. The effect is minute—it causes the star to move back and forth by no more than 51 centimetres per second (1.8 km/hour), about the speed of a baby crawling. This is the highest precision ever achieved using this method.
Alpha Centauri B is very similar to the Sun but slightly smaller and less bright. The newly discovered planet, with a mass of a little more than that of the Earth, is orbiting about six million kilometres away from the star, much closer than Mercury is to the Sun in the Solar System. The orbit of the other bright component of the double star, Alpha Centauri A, keeps it hundreds of times further away, but it would still be a very brilliant object in the planet's skies.
This video shows an imaginary journey from Earth to the Alpha Centauri system. As we leave the Solar System we see the familiar constellation figures including the Southern Cross (Crux) and the bright stars Alpha and Beta Centauri. As we approach Alpha Centauri we pass a faint red star, this is Proxima Centauri, the closest star to Earth and the faintest component of a triple star system. The final part shows the bright double star Alpha Centauri A and B with the Sun visible in the background. Alpha Centauri B is known to be orbited by an Earth-mass planet, the closest exoplanet to the Solar System. Credit: ESO./L. Calçada/Nick Risinger
The first exoplanet around a Sun-like star was found by the same team back in 1995 and since then there have been more than 800 confirmed discoveries, but most are much bigger than the Earth, and many are as big as Jupiter. The challenge astronomers now face is to detect and characterise a planet of mass comparable to the Earth that is orbiting in the habitable zone around another star. The first step has now been taken.
"This is the first planet with a mass similar to Earth ever found around a star like the Sun. Its orbit is very close to its star and it must be much too hot for life as we know it," adds Stéphane Udry (Geneva Observatory), a co-author of the paper and member of the team, "but it may well be just one planet in a system of several. Our other HARPS results, and new findings from Kepler, both show clearly that the majority of low-mass planets are found in such systems."
"This result represents a major step towards the detection of a twin Earth in the immediate vicinity of the Sun. We live in exciting times!" concludes Xavier Dumusque.
More information: DOI: 10.1038/nature11572
Journal information: Nature
Provided by ESO