Carbon stored in Arctic tundra could be released into the atmosphere by new trees growing in the warmer region, exacerbating climate change, scientists have revealed.
The Arctic is getting greener as plant growth increases in response to a warmer climate. This greater plant growth means more carbon is stored in the increasing biomass, so it was previously thought the greening would result in more carbon dioxide being taken up from the atmosphere, thus helping to reduce the rate of global warming.
However, research published in Nature Climate Change, shows that, by stimulating decomposition rates in soils, the expansion of forest into tundra in arctic Sweden could result in the release of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere.
Dr Iain Hartley now based in Geography at the University of Exeter, and lead author of the paper, said: "Determining directly how carbon storage is changing in high-latitude ecosystems is very difficult because the majority of the carbon present is stored below ground in the soils. Our work indicates that greater plant biomass may not always translate into greater carbon storage at the ecosystem level.
"We need to better understand how the anticipated changes in the distribution of different plant communities in the Arctic affects the decomposition of the large carbon stocks in tundra soils if we are to be able to predict how arctic greening will affect carbon dioxide uptake or release in the future."
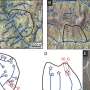
By measuring carbon stocks in vegetation and soils between tundra and neighbouring birch forest, it was shown that compared to tundra, the two-fold greater carbon storage in plant biomass in the forest was more than outweighed by the smaller carbon stocks in forest soils.
Furthermore, using a novel methodology based on measuring the radiocarbon content of the carbon dioxide being released, the researchers found that the birch trees appeared to be stimulating the decomposition of soil organic matter. Thus, the research was able to identify a mechanism by which the birch trees can contribute directly to reducing carbon storage in soils.
"Dr Gareth Phoenix, of the University of Sheffield's Department Animal and Plant Sciences, who collaborated on the research, added:
"It shows that the encroachment of trees onto Arctic tundra caused by the warming may cause large release of carbon to the atmosphere, which would be bad for global warming.
"This is because tundra soil contains a lot of stored organic matter, due to slow decomposition, but the trees stimulate the decomposition of this material. So, where before we thought trees moving onto tundra would increase carbon storage it seems the opposite may be true. So, more bad news for climate change."
The results of the study are in sharp contrast to the predictions of models which expect total carbon storage to increase with the greater plant growth. Rather, this research suggests that colonisation by productive, high-biomass, plant communities in the Arctic may not always result in greater capture of carbon dioxide, but instead net losses of carbon are possible if the decomposition of the large carbon stocks in Arctic soils are stimulated. This is important as Arctic soils currently store more carbon than is present in the atmosphere as carbon dioxide and thus have considerable potential to affect rates of climate change. It is yet to be seen whether this observed pattern is confined to certain soil conditions and colonising tree species, or whether the carbon stocks in the soils of other arctic or alpine ecosystems may be vulnerable to colonisation by new plant communities as the climate continues to warm.
Journal information: Nature Climate Change
Provided by University of Exeter